AWS: The accomplished guide to Amazon Web Services you need – Part 1
In the current age of cloud computing, there is now a multitude of mature services available — offering security, scalability, and reliability for many business computing needs. What was once a colossal undertaking to build a data center, install server racks, and design storage arrays has given way to an entire marketplace of services that are always just a click away.
One leader in that marketplace is Amazon Web Services, which consists of 175 products and services in a vast catalog that provides cloud storage, compute power, app deployment, user account management, data warehousing, tools for managing and controlling the Internet of Things devices, and just about anything you can think of that a business needs.
AWS really grew in popularity and capability over the last decade. One reason is that AWS is so reliable and secure. It’s a gold standard and used by some of the most well-known brands in existence, such as Netflix, Uber, and Airbnb. What started as primarily a cloud infrastructure for computing power and storage evolved and scaled quickly (like the service offerings themselves) as companies kept looking for more and more products to help them do business
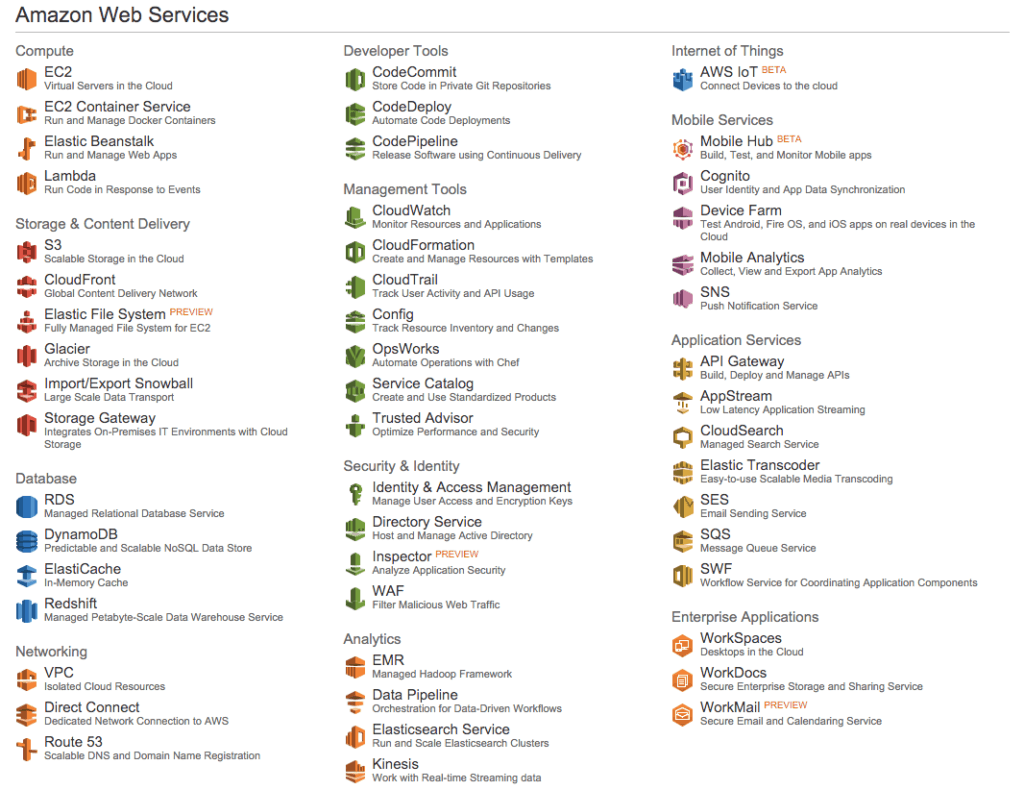
Part 1: List of Amazon Web Services (AWS) services
The following Amazon Web Services are available:
AWS AMI: An AWS AMI (Amazon Machine Image) allows you to deploy instances in the cloud. In simple terms, it is like the portion of a local server in a data center or like a virtual machine that runs in the cloud. Without an AMI, the advantages of cloud computing really would not be possible.
AWS AppSync: AppSync is a cloud-based service that keeps mobile and web apps up to date, but only as needed and only at the scale you need for your particular needs. It uses a cost structure that is designed to maintain only critical data and leave data at rest untouched.
Amazon Athena: For companies that house their data in the cloud using a service like Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service), Amazon Athena is a godsend. It’s a query service that allows you to run SQL queries in the cloud, which means there’s no need to operate a local database.
Amazon Aurora: For those who need to deploy a relational database in the cloud, there is one main option from Amazon called Aurora. This means you can rely on a high-performance database that can keep up with the needs of your applications.
AWS Batch: One of the key advantages to the cloud is that the infrastructure can scale as your needs change. AWS Batch is a batch processing service for Big Data projects. As your projects increase in size, the cloud infrastructure supporting it can adapt.
AWS CLI: AWS CLI (Command Line Interface) is a downloadable application you can use to control AWS functions. This command line introduces a new, powerful way to form commands, while making it simple for team members to execute them.
AWS CloudFormation: For companies that need to deploy and manage application stacks and resource, AWS CloudFormation is a way to “form the cloud” so that you can deploy web and mobile apps easily. For managing the cloud, you can use one main command line interface.
AWS CloudFront: A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is normally a difficult undertaking for companies to develop and deploy. AWS CloudFront is a CDN that runs in the cloud and can scale as your media streaming, messaging, and file distribution needs change and evolve.
AWS CodeDeploy: This service allows you to deploy apps in a cloud environment, such as Amazon EC2, AWS Fargate, AWS Lambda, or your on-premise infrastructure. It means faster, more efficient deployment for companies that want to reach a market segment faster.
AWS CodePipeline: Modern application development is a complex undertaking, but AWS CodePipeline allows companies to manage all of the steps involved, from building, testing, and production. It’s an efficient method because of a single point of management and control.
AWS Cognito: User account control is easy when it is part of a brand new app. You might only have a few dozen users. AWS Cognito can help when you start scaling up to hundreds, thousands, or even millions of users, helping with the management and authentication.
Amazon Connect: Amazon Connect is the ultimate way to improve customer service, especially for small businesses. It uses the cloud in order to save storage, it’s pay-as-you-go, and efficient and simple to navigate.
AWS Console: AWS Console is the primary source of controlling the services you use, scaling your cloud environment, and even deploying new services. It is like a one-stop-shop for cloud computing needs. AWS Console is extremely fast, easy to use, and even offers support assistance if one of your services isn’t working properly.
Amazon Corretto: A production-ready distribution of OpenJDK, Amazon Corretto allows you to create, run, and deploy Java applications in the cloud. It’s designed to make this process more efficient and scalable so that you don’t have to overhaul your infrastructure.
AWS Data Pipeline: Data transformation is a term that can make your head spin, especially if you are in charge of the migration. AWS Data Pipeline makes this much more fluid and efficient, even if you are migrating and moving data in a complex environment.
AWS Direct Connect: AWS Direct Connect is a bridge between the old and the new. It’s a service that connects legacy and non-critical data to data stores that are actively deployed for your applications and infrastructure. The data becomes available for apps in real-time.
Amazon DynamoDB: Any garden-variety database running on a server just won’t cut it in the modern age of complex apps for the web and mobile devices. Amazon DynamoDB is a high-performance database that runs in the cloud, with all of the advantages of scale and reliability you’d expect.
AWS EBS: AWS EBS (Elastic Block Store) is a cloud service that allows you to store files in the more traditional block storage format that has existed for decades, which is helpful for legacy apps, Big Data projects, or archiving purposes.
Amazon EC2: Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) provides an IT infrastructure that runs in the cloud. It offers power, flexibility, and performance all at the same time. The biggest benefit of EC2 is that it offers quick, efficient scalability for users.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk: As the name implies, Elastic Beanstalk provides an adaptable, flexible way to scale applications without the usual setup, management, and configuration of the server infrastructure. It’s elastic in the sense that it can adapt and scale to your business needs.
Amazon EMR: Amazon Elastic MapReduce is a service for deploying the frameworks needed to do Big Data analytics in the cloud. It is often used for genomic research, drug discovery, analyzing materials used for new products, and other tests that require massive data analysis.
AWS Fargate: AWS Fargate is Amazon’s serverless compute engine that makes it easier than ever to update or develop an application without fear of a data breach so that you’re constantly keeping up with new infrastructure demands.
AWS Glue: With AWS Glue, there’s no need for advanced technology in order to keep all of your data in one place. AWS Glue is the “glue” that ties together different kinds of data, making it readily available for queries.
Amazon Kinesis: Amazon Kinesis provides real-time analytics for data as it flows in your cloud infrastructure. The service provides real-time analytics and reporting functions. The real power of Kinesis is that it can keep up with your apps and scale accordingly.
AWS Lambda: AWS Lambda is a computing service provided by Amazon that processes code and automatically operates computing resources as needed. As a cloud-based service, there is never a need to worry about power or storage.
Amazon Lightsail: Amazon Lightsail is a framework that allows developers to run applications on virtual servers in the cloud. Because it is a secure environment and is a compliment to other Amazon services like Elastic Compute Cloud (ECS2), it has a powerful use case.
AWS Outposts: What if you could run a replica of the cloud services Amazon offers, but in your own data center? That’s the idea behind AWS Outposts, a service that provides all of the features and functions of cloud services but in your local infrastructure.
Amazon RDS: Amazon RDS helps companies store relational databases in the cloud. It can be used for analytics, business dashboards, web applications, or any app that uses a relational database. This provides added flexibility and an ability to scale to your needs.
Amazon Redshift: Amazon Redshift is an online data warehouse that provides its users with flexibility, ease of navigation, security, automatic updates — and it’s just as effective for large businesses as it is small ones.
Amazon S3: A well-known object storage service, Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a powerful, scalable, reliable service that meets the demands of even the most complex enterprise-grade apps and the largest companies and institutions.
Amazon SES: Amazon SES (Simple Email Service) is the best way to improve messaging. It’s pay-as-you-go, and it is designed to fit right into the current IT infrastructure your business uses. It can send several thousand messages without concerns about security or performance.
AWS Snowball: AWS Snowball is a data transfer service that helps businesses perform more secure data migration. The data being moved will not go through the Internet, so the migration is quicker, safer, and more reliable if you want to access the information later on. Snowball is extremely scalable, allowing businesses to transport any amount of data they need.
Amazon SNS: Modern applications are constantly communicating with servers and each other. Even simple changes like a new high-score in the gaming app have to be transmitted. Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) manages, tracks, and controls these messages.
Amazon SQS: Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) is a message queuing service that runs independently of the actual infrastructure you are using. It makes sure messages between servers and apps run efficiently, securely, and reliably.
AWS Step Functions: “Step Functions” allows developers to create apps that use multiple transactional services. Previous to cloud computing services such as Step Functions, linking to multiple sources was much more complex, which caused issues with reliability.
AWS Storage Gateway: AWS Storage Gateway is a hybrid storage option for companies with legacy data stores but who also are taking advantage of cloud storage. The service bridges the gap between the two, providing one console to control and manage both data stores.
AWS VPC: AWS VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) is, as the name implies, a secure virtual cloud that can help ease the minds of business owners launching a new website, app, or other services. AWS VPC is a separate portion of the Amazon cloud that offers a lot of flexibility and scalability.
AWS WAF: Not all firewalls run as a hardware device in a data center. AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) is a cloud-based firewall you use to protect apps and data in the cloud. Companies can add or remove cloud security features depending on their needs.
AWS X-Ray: One of the most curiously named products from Amazon, X-Ray should not be confused with the Amazon Prime Video service for finding out more about actors. It’s a cloud service that tracks and manages all of the messaging that occurs between cloud-based apps.
Continue on part 2: https://cloudspace.vn/blog/amazon-web-services-aws-guide-2/
Gathered by @cloudspacevn